Cartesi : The Blockchain OS

Key Takeaway
Let's delve into the concept of blockchain operating systems (OS) and explore why Cartesi stands out among other layer 2 solutions. Additionally, we'll take a closer look at the $CTSI tokenomics.
Disclaimer: This is NOT financial advice NOR sponsored content
Introduction
Cartesi is a Layer-2 platform that brings Linux and traditional software tools to blockchains. It enables developers to run any full-stack software on a blockchain, including operating systems, programming languages, compilers, and libraries. This opens up a world of possibilities for decentralized applications (DApps), as it allows them to be developed using the same tools and technologies that are used for traditional software.
Cartesi uses a rollup architecture to achieve scalability and security. Rollups are a type of Layer-2 scaling solution that allows DApps to execute computations off-chain and then post the results on-chain. This significantly reduces the amount of data that needs to be processed on-chain, which in turn reduces transaction fees and increases scalability.
What's Blockchain Rollup?
A rollup is a blockchain scalability solution that moves complex computations off the main network (layer 1), such as the Ethereum network, and onto a separate computing environment (layer 2). When using rollups, the blockchain's role is limited to receiving and logging transactions. In rare cases where parties disagree on the outcome of computation, the blockchain is also involved in resolving disputes.
Rollups Solutions
Rollups are a type of Layer 2 scaling solution that executes transaction computations off-chain. This means that the computations are not carried out by the main blockchain, but instead in a separate computation environment. The rollup protocol ensures the validity of transactions via either validity proofs or fraud proofs.
Rollups are able to compress data from several transactions into a bundle, which decreases both transaction costs and size. This increases overall efficiency.
By offloading computations to a separate environment and compressing data, rollups can scale blockchains while keeping the security guarantees of their consensus mechanism.
Cartesi Rollups
Cartesi's version of Optimistic Rollups uses interactive fraud proofs, which allows for larger computations to be executed off-chain. This is because the blockchain only needs to verify a single instruction in the event of a dispute, rather than the entire computation. As a result, Cartesi's rollups can support more complex applications and data-intensive workloads and more importantly, Cartesi supports many types of programming languages rather than just Solidity or Vyper on EVM
Token Allocation and Vesting Schedule
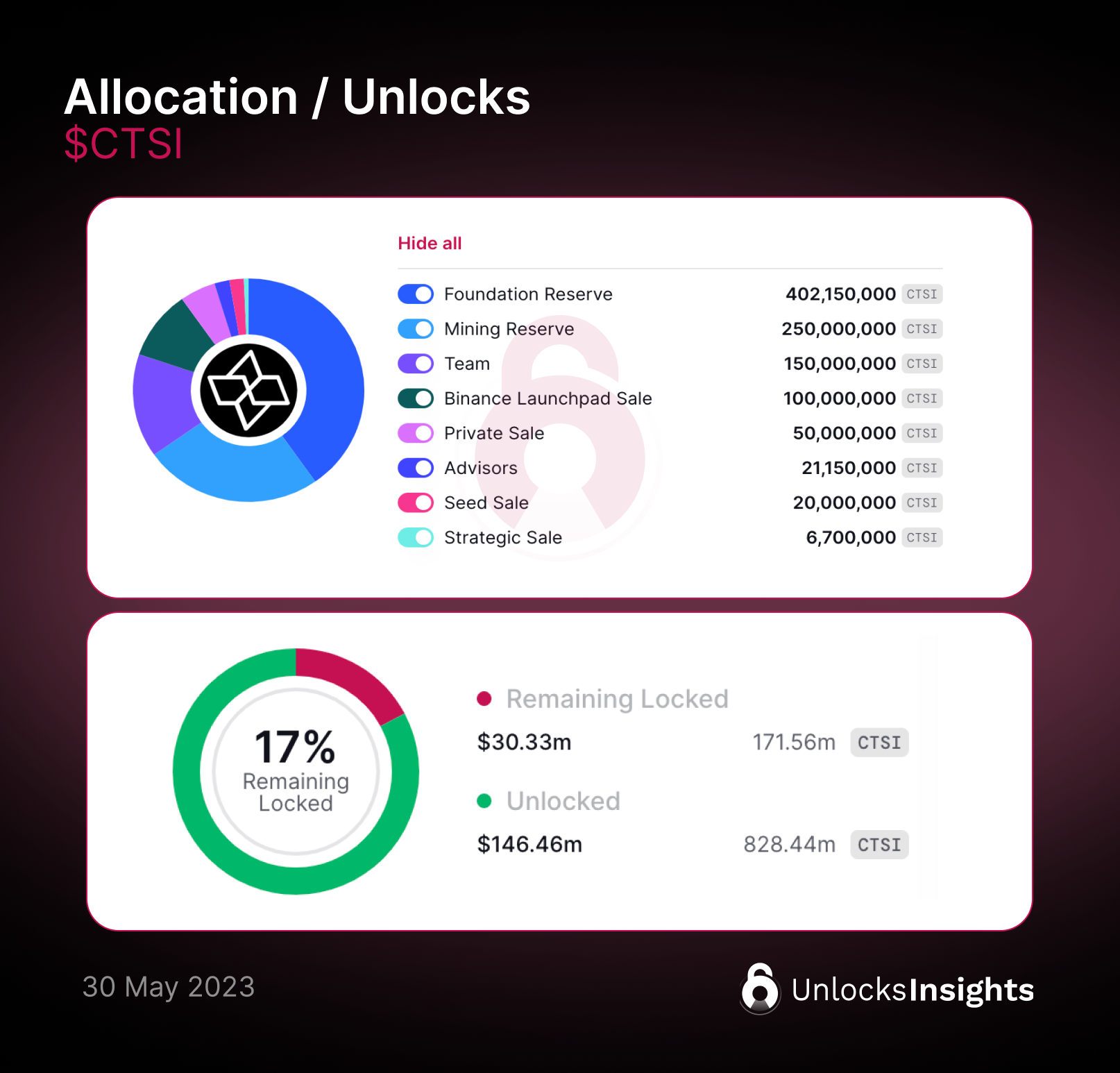
Cartesi's native token, $CSTI, was allocated through multiple sale rounds, as shown in the token allocation chart. Many of these tokens were fully unlocked as Cartesi launched in April 2020. Currently remaining locked at around 17% of the total supply, which only the Mining Reserve and Team tokens remain locked.
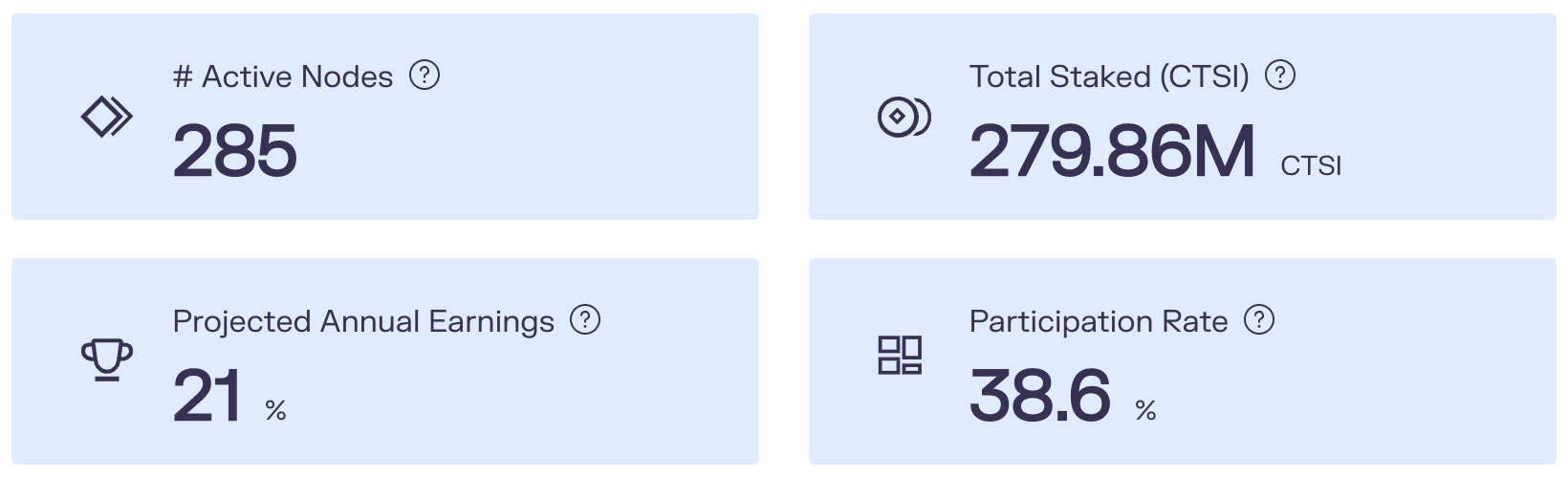
The mining reserve is a reward program for people who stake $CTSI. Currently, the APR is 21%, which is considerably high. The staking ratio, or participation rate, is still under 40%. This means that there is still a significant opportunity for people to earn rewards by staking $CTSI.
Another portion of the tokens is allocated to the team. Two more cliff unlocks are expected to occur for this portion, one in October and one in April of next year.

Transparency
The Cartesi team released a report to the public in April 2023, following the last unlock. This report demonstrates the team's commitment to transparency, as well as their ongoing efforts to keep the community informed such as the Ecosystems update, or the recent ETHGlobal Lisbon 2023 which they also attended

Conclusion
Cartesi is a Layer-2 platform that enables developers to run any full-stack software on a blockchain by using optimistic rollups. This means that developers can use the same tools and technologies that they are used to, such as Linux, programming languages, compilers, and libraries. This opens up a world of possibilities for decentralized applications (DApps), as it allows them to be developed more easily and efficiently.
Since the Cartesi token ($CSTI) was launched in April 2020, the majority of the tokens have been unlocked (83% of the total supply). Only a small portion of the tokens, which are allocated to the team, are still locked and will be unlocked in October and April. This means that there is currently low selling pressure on the $CSTI.
The Cartesi team actively updates their progress on their Medium blog, which provides more transparency on their work. This includes information about the unlocked token, which occurred in April.
Reference